Archive for the ‘Skin Stem Cells’ Category
Eggs created from stem cells in fertility breakthrough
Professor Robert Norman, Professor of Reproductive Medicine at the University of Adelaide in Australia, said: "While this is a major contribution to knowledge, application to humans is still a long way off but for the first time the goal appears to be in sight.
In the new study, the scientists transformed skin cells into personalised stem cells, which were then fertilised via IVF and ultimately resulted in three fertile baby mice.
Safety concerns must be addressed, particularly into the long-term health of the resulting offspring, before researchers come any closer to determining whether the treatment could be viable in humans.
The researchers wrote in the latest online issue of the journal Science: "Our system serves as a robust foundation to investigate and further reconstitute female germ line development in vitro (in the laboratory), not only in mice, but also in other mammals, including humans."
Dr Allan Pacey, senior lecturer in reproduction and developmental medicine at the University of Sheffield, said: "What is remarkable about this work is the fact that, although the process is still quite inefficient, the offspring appeared healthy and were themselves fertile as adults.
"This is a great step forward, but I would urge caution as this is a laboratory study and we are still quite a long way from clinical trials taking place in humans."
Read more from the original source:
Eggs created from stem cells in fertility breakthrough
Eggs can be created from skin cells
Eggs capable of being fertilised and making babies can be created in the laboratory from skin cells, a study has shown.
Scientists successfully produced three fertile baby mice using the technique, which involves transforming ordinary skin cells into personalised stem cells.
The same Japanese team created viable mouse sperm from embryonic stem cells earlier this year.
Together, both advances greatly increase the likelihood of radical and controversial future treatments for restoring fertility. It could mean creating sperm for men whose fertility has been wiped out by cancer therapy or reversing the menopause in women long after they have used up their natural supply of eggs.
In August, scientists from Kyoto University in Japan announced that they had created sperm cells from mouse embryo stem cells. Injected into mouse eggs, the sperm produced embryos which developed into healthy baby mice.
The same team, led by Dr Katsuhiko Hayashi, carried out the latest research which focused on eggs rather than sperm. The scientists mirrored their earlier achievement by transforming stem cells from mouse embryos into eggs which could be fertilised to produce offspring. But they also took a further step by obtaining mouse pups from eggs derived from ordinary skin cells.
The researchers wrote in the latest online issue of the journal Science: "Our system serves as a robust foundation to investigate and further reconstitute female germline development in vitro (in the laboratory), not only in mice but also in other mammals, including humans."
The "germline" consists of genetic material carried in reproductive cells that can be passed onto future generations.
Dr Allan Pacey, senior lecturer in reproduction and developmental medicine at the University of Sheffield, said: "This is a very technical piece of work which pushes much further the science of how eggs are generated and how we might one day be able to routinely stimulate the new production of eggs for women who are infertile.
"What is remarkable about this work is the fact that, although the process is still quite inefficient, the offspring appeared healthy and were themselves fertile as adults. This is a great step forward but I would urge caution as this is a laboratory study and we are still quite a long way from clinical trials taking place in humans."
Go here to read the rest:
Eggs can be created from skin cells
Baby Mice Born from Eggs Made from Stem Cells
Mouse pups from induced pluripotent stem cell-derived eggs; image courtesy of Katsuhiko Hayashi
Stem cells have been coaxed into creating everything from liver cells to beating heart tissue. Recently, these versatile cells were even used to make fertile mouse sperm, suggesting that stem cell technology might eventually be able to play a role in the treatment of human infertility.
Now two types of stem cells have been turned into viable mouse egg cells that were fertilized and eventually yielded healthy baby mice. Details of this achievement were published online October 4 in Science.
Mouse oocytes; image courtesy of Katsuhiko Hayashi
Katsuhiko Hayashi, of Kyoto Universitys School of Medicine, were able to create the eggs with embryonic stem cells as well as with induced pluripotent stem cells (formed from adult cells).
The team started with female embryonic stem cells and then coaxed them genetically to revert to an earlier developmental stage (primordial germ cell-like cells). These cells were blended with gonadal somatic cells, important in the development of sexual differentiation, to create reconstituted ovaries. The researchers then transplanted these cultured assemblages into female mice (in either the actual ovary or the kidney) for safekeeping and to allow the stem cells to mature into oocytes in a natural environment.
Healthy adult mice from litter produced from induced pluripotent stem cell-based oocytes; image courtesy of Katsuhiko Hayashi
To test the eggs fertility, the new oocytes were removed from the mice for an in vitro fertilization with mouse spermand then re-implanted into the female mice. The experimental females went on to bear normally developing and fertile offspring. The procedure was then also performed successfully with induced pluripotent stem cells from adult skin cells with similar results.
Our system serves as a robust foundation to investigate and further reconstitute female germline development in vitro, the researchers noted in their paper, not only in mice, but also in other mammals, including humans.
Read more from the original source:
Baby Mice Born from Eggs Made from Stem Cells
Skin care simplified
Are you stumped by the multitude of ingredients in skin care products? Are you baffled by even the basic lotions and potions available on the market?
If so, then here is our fool proof guide to getting the best out of your skin care purchases.
Here are the products to look out for in each stage of you skin's development.
From 18 years
What you are looking for depends on your skin. Usually young skin needs either hydration or sebum-regulation, or possibly both. For moisturisation, look for trehalose, amino acids, hyaluronic acid or urea. If you want to rid your skin of excess oils, go for azeliac acid, clay or black popular.
25-35 years
Women this age need to bring lipids to the skin. Omega 3 and 5 and ceramides are great, too. Look for vegetal stem cells to improve the energy of cells and the cell turnover and antioxidants such as lipoic acid, vitamin E and C to prevent ageing. Exfoliate with AHA or PHA.
35-45 years
Look for active anti-ageing ingredients that can boost your own elastin and hyaluronic acid. Peptides are great, as is stem-cells from apple or edelweiss as they have antioxidative properties and improve the synthesis of collagen and elastine.
45 years up
The rest is here:
Skin care simplified
Blind Mice Get Experimental Stem Cell Treatment For Blindness
April Flowers for redOrbit.com Your Universe Online
Columbia University ophthalmologists and stem cell researchers have developed an experimental treatment for blindness using the patients skin cells, which has improved the vision of blind mice in testing.
The findings of this research, published online in the journal Molecular Medicine, suggest that induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) could soon be used to improve vision in people with macular degeneration and other eye retina diseases. iPS cells are derived from adult human skin cells but have embryonic qualities.
With eye diseases, I think were getting close to a scenario where a patients own skin cells are used to replace retina cells destroyed by disease or degeneration, says Stephen Tsang, MD, PhD, associate professor of ophthalmology and pathology & cell biology. Its often said that iPS transplantation will be important in the practice of medicine in some distant future, but our paper suggests the future is almost here.
Scientists were very excited by the advent of human iPS cells when they were discovered in 2007, as they provide a way to avoid the ethical complications of embryonic stem cells. Another advantage is that the iPS cells are created from the patients own skin, eliminating the need for anti-rejection medications. Like the ethically challenged embryonic cells, iPS cells can develop into any type of cell. To-date, no iPS cells have been implanted into people, but many ophthalmologists say that the eye would prove to be ideal testing ground for iPS therapies.
The eye is a transparent and accessible part of the central nervous system, and thats a big advantage. We can put cells into the eye and monitor them every day with routine non-invasive clinical exams, Tsang said. And in the event of serious complications, removing the eye is not a life-threatening event.
Professor Tsang is running a new preclinical iPS study using human iPS cells derived from the skin cells of a 53-year-old donor. The cells were first transformed with a cocktail of growth factors into cells in the retina that lie underneath the eyes light-sensing cells.
Retina cells nourish the light-sensing cells and protect the fragile cells from excess light, heat and cellular debris. In macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa, retina cells die, which allows the photoreceptor cells to degenerate causing the patient to lose their vision. It is estimated that 30 percent of people will have some form of macular degeneration by the time they are 75 years old, as it is the leading cause of vision loss in the elderly. Currently, it affects 7 million Americans and that is expected to double by 2020.
The Columbia research team injected the iPS-derived retina cells into the right eyes of 34 mice that had a genetic mutation that caused their retina cells to degenerate. In many of the mice, the iPS cells assimilated into the retina without disruption and functioned as normal retina cells well into the animals old age. Mice in the control group, who received injections of saline or inactive cells, showed no improvement in retina tests.
Our findings provide the first evidence of life-long neuronal recovery in a preclinical model of retinal degeneration, using stem cell transplant, with vision improvement persisting through the lifespan, Tsang says. And importantly, we saw no tumors in any of the mice, which should allay one of the biggest fears people have about stem cell transplants: that they will generate tumors.
Continued here:
Blind Mice Get Experimental Stem Cell Treatment For Blindness
Patients’ own skin cells could restore vision in elderly with macular degeneration
Washington, October 2 (ANI): A new study has suggested that induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells - which are derived from adult human skin cells but have embryonic properties - could soon be used to restore vision in people with macular degeneration and other diseases that affect the eye's retina.
In the study conducted by Columbia ophthalmologists and stem cell researchers, adult stem cells developed from a patient's skin cells improved the vision of blind mice.
"With eye diseases, I think we're getting close to a scenario where a patient's own skin cells are used to replace retina cells destroyed by disease or degeneration," said the study's principal investigator, Stephen Tsang, MD, PhD, associate professor of ophthalmology and pathology and cell biology.
"It's often said that iPS transplantation will be important in the practice of medicine in some distant future, but our paper suggests the future is almost here," he stated.
The advent of human iPS cells in 2007 was greeted with excitement from scientists who hailed the development as a way to avoid the ethical complications of embryonic stem cells and create patient-specific stem cells.
Like embryonic stem cells, iPS cells can develop into any type of cell. Thousands of different iPS cell lines from patients and healthy donors have been created in the last few years, but they are almost always used in research or drug screening.
In Tsang's new preclinical iPS study, human iPS cells - derived from the skin cells of a 53-year-old donor - were first transformed with a cocktail of growth factors into cells in the retina that lie underneath the eye's light-sensing cells.
The primary job of the retina cells is to nourish the light-sensing cells and protect the fragile cells from excess light, heat, and cellular debris. If the retina cells die - which happens in macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa - the photoreceptor cells degenerate and the patient loses vision.
Macular degeneration is a leading cause of vision loss in the elderly, and it is estimated that 30 percent of people will have some form of macular degeneration by age 75.
In their study, the researchers injected the iPS-derived retina cells into the right eyes of 34 mice that had a genetic mutation that caused their retina cells to degenerate.
See the original post here:
Patients' own skin cells could restore vision in elderly with macular degeneration
Patients' own skin cells could restore vision in elderly with macular degeneration
Washington, October 2 (ANI): A new study has suggested that induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells - which are derived from adult human skin cells but have embryonic properties - could soon be used to restore vision in people with macular degeneration and other diseases that affect the eye's retina.
In the study conducted by Columbia ophthalmologists and stem cell researchers, adult stem cells developed from a patient's skin cells improved the vision of blind mice.
"With eye diseases, I think we're getting close to a scenario where a patient's own skin cells are used to replace retina cells destroyed by disease or degeneration," said the study's principal investigator, Stephen Tsang, MD, PhD, associate professor of ophthalmology and pathology and cell biology.
"It's often said that iPS transplantation will be important in the practice of medicine in some distant future, but our paper suggests the future is almost here," he stated.
The advent of human iPS cells in 2007 was greeted with excitement from scientists who hailed the development as a way to avoid the ethical complications of embryonic stem cells and create patient-specific stem cells.
Like embryonic stem cells, iPS cells can develop into any type of cell. Thousands of different iPS cell lines from patients and healthy donors have been created in the last few years, but they are almost always used in research or drug screening.
In Tsang's new preclinical iPS study, human iPS cells - derived from the skin cells of a 53-year-old donor - were first transformed with a cocktail of growth factors into cells in the retina that lie underneath the eye's light-sensing cells.
The primary job of the retina cells is to nourish the light-sensing cells and protect the fragile cells from excess light, heat, and cellular debris. If the retina cells die - which happens in macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa - the photoreceptor cells degenerate and the patient loses vision.
Macular degeneration is a leading cause of vision loss in the elderly, and it is estimated that 30 percent of people will have some form of macular degeneration by age 75.
In their study, the researchers injected the iPS-derived retina cells into the right eyes of 34 mice that had a genetic mutation that caused their retina cells to degenerate.
Continued here:
Patients' own skin cells could restore vision in elderly with macular degeneration
Stem cells improve visual function in blind mice
Public release date: 1-Oct-2012 [ | E-mail | Share ]
Contact: Elizabeth Streich estreich@columbia.edu 212-305-3689 Columbia University Medical Center
An experimental treatment for blindness, developed from a patient's skin cells, improved the vision of blind mice in a study conducted by Columbia ophthalmologists and stem cell researchers.
The findings suggest that induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells which are derived from adult human skin cells but have embryonic properties could soon be used to restore vision in people with macular degeneration and other diseases that affect the eye's retina.
"With eye diseases, I think we're getting close to a scenario where a patient's own skin cells are used to replace retina cells destroyed by disease or degeneration," says the study's principal investigator, Stephen Tsang, MD, PhD, associate professor of ophthalmology and pathology & cell biology. "It's often said that iPS transplantation will be important in the practice of medicine in some distant future, but our paper suggests the future is almost here."
The advent of human iPS cells in 2007 was greeted with excitement from scientists who hailed the development as a way to avoid the ethical complications of embryonic stem cells and create patient-specific stem cells. Like embryonic stem cells, iPS cells can develop into any type of cell. Thousands of different iPS cell lines from patients and healthy donors have been created in the last few years, but they are almost always used in research or drug screening.
No iPS cells have been transplanted into people, but many ophthalmologists say the eye is the ideal testing ground for iPS therapies.
"The eye is a transparent and accessible part of the central nervous system, and that's a big advantage. We can put cells into the eye and monitor them every day with routine non-invasive clinical exams," Tsang says. "And in the event of serious complications, removing the eye is not a life-threatening event."
In Tsang's new preclinical iPS study, human iPS cells derived from the skin cells of a 53-year-old donor were first transformed with a cocktail of growth factors into cells in the retina that lie underneath the eye's light-sensing cells.
The primary job of the retina cells is to nourish the light-sensing cells and protect the fragile cells from excess light, heat, and cellular debris. If the retina cells die which happens in macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa the photoreceptor cells degenerate and the patient loses vision. Macular degeneration is a leading cause of vision loss in the elderly, and it is estimated that 30 percent of people will have some form of macular degeneration by age 75. Macular degeneration currently affects 7 million Americans and its incidence is expected to double by 2020.
Read the rest here:
Stem cells improve visual function in blind mice
Grand Forks firm stores human cells for future treatments
GRAND FORKS The goal of a Grand Forks start-up is to get customers to prepare for a future in which todays medical breakthroughs based on stem cells are commonplace.
You would ordinarily think this is science fiction, said Vin Singh, founder of Next Healthcare, based at UNDs Center for Innovation.
Singh is referring to developments in regenerative medicine in which researchers have used stem cells to re-grow lung, cornea and trachea cells and create other types of human tissue. These advances point to a future when replacing organs will become a common medical procedure.
And he wants people to act now.
Singhs business, which he has been building since 2009 and launched this past spring, is a cell bank, storing samples of clients skin, blood and bone marrow cells for future use when regenerative treatments are improved and widespread.
We know some of them are going to work, and were betting that youre going to be able to use some of your cells, Singh said. If and when those therapies come on line, you will have that healthy seed.
Betting on future
Singhs resume lists a number of companies in the biomedical field. But the basis of his new business is essentially storage, freezing samples of clients tissue that could be used by doctors to treat future health problems.
Clients doctors collect their tissue samples and send them to Next Healthcare in Grand Forks, where they are stored frozen. The company is based in UNDs REAC building, which provides biocontainment facilities. Next Healthcare also has a second storage facility in North Dakota at an undisclosed location, Singh said.
The key to therapies that Singhs company is betting on and wants prospective customers to bet on are advances within the past decade that have manipulated non-stem cells from skin or blood to mimic stem cells ability to grow into different types of tissues.
View post:
Grand Forks firm stores human cells for future treatments
Researchers find multiple similarities between cancer cells and induced pluripotent stem cells
Public release date: 28-Sep-2012 [ | E-mail | Share ]
Contact: Charles Casey charles.casey@ucdmc.ucdavis.edu 916-734-9048 University of California - Davis Health System
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) UC Davis investigators have found new evidence that a promising type of stem cell now being considered for a variety of disease therapies is very similar to the type of cells that give rise to cancer. The findings suggest that although the cells -- known as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) -- show substantial promise as a source of replacement cells and tissues to treat injuries, disease and chronic conditions, scientists and physicians must move cautiously with any clinical use because iPSCs could also cause malignant cancer.
The article, "Induced pluripotency and oncogenic transformation are related processes," is now online in the journal, Stem Cells and Development.
"This is the first study that describes the specific molecular pathways that iPSCs and cancer cells share from a direct comparison" said Paul Knoepfler, associate professor of cell biology and human anatomy, and principal investigator of the study. "It means that much more study is required before iPSCs can be used clinically. However, our study adds to a growing knowledge base that not only will help make stem cell therapies safer, but also provide us with new understandings about the cancer-causing process and more effective ways to fight the disease."
Since 2007, cell biologists have been able to induce specialized, differentiated cells (such as those obtained from the skin or muscle of a human adult) to become iPSCs. Like embryonic stem cells, iPSCs are a type of stem cell that is able to become any cell type. This "pluripotent" capability means that iPSCs have the potential of being used in treatments for a variety of human diseases, a fundamentally new type of clinical care known as regenerative medicine.
iPSCs are considered particularly important because their production avoids the controversy that surrounds embryonic stem cells. In addition, iPSCs can be taken from a patient's own skin and induced to produce other needed tissues, thereby evading the possibility of immunologic rejection that arises when transplanting cells from a donor to a recipient. In contrast to therapies based on ES cells, iPSCs would eliminate the need for patients to take immunosuppressive drugs.
Earlier research indicated that both ES cells and iPSCs pose some health risks. Increasing evidence suggests that pluripotency may be related to rapid cellular growth, a characteristic of cancer. iPSCs, as well as embryonic stem cells, are well known by scientists to have the propensity to cause teratomas, an unusual type of benign tumor that consists of many different cell types. The new UC Davis study demonstrates for the first time that iPSCs -- as well as ES cells -- share significant similarities to malignant cancer cells.
The investigators compared iPSCs to a form of malignant cancer known as oncogenic foci that are also produced in laboratories; these cell types are used by medical researchers to create models of cancer, particularly sarcoma. Specifically, the scientists contrasted the different cells' transcriptomes, comprised of the RNA molecules or "transcripts." Unlike DNA analysis, which reflects a cell's entire genetic code whether or not the genes are active, transcriptomes reflect only the genes that are actively expressed at a given time and therefore provide a picture of actual cellular activity.
From this transcriptome analysis, the investigators found that the iPSCs and malignant sarcoma cancer cells are unexpectedly similar in several respects. Genes that were not expressed in iPSCs were also not expressed in the cancer-generating cells, including many that have properties that guide a cell to normally differentiate in certain directions. Both cell types also exhibited evidence of similar metabolic activities, another indication that they are related cell types.
Here is the original post:
Researchers find multiple similarities between cancer cells and induced pluripotent stem cells
Multiple similarities discovered between cancer cells and induced pluripotent stem cells
ScienceDaily (Sep. 28, 2012) UC Davis investigators have found new evidence that a promising type of stem cell now being considered for a variety of disease therapies is very similar to the type of cells that give rise to cancer. The findings suggest that although the cells -- known as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) -- show substantial promise as a source of replacement cells and tissues to treat injuries, disease and chronic conditions, scientists and physicians must move cautiously with any clinical use because iPSCs could also cause malignant cancer.
The article, "Induced pluripotency and oncogenic transformation are related processes," is now online in the journal, Stem Cells and Development.
"This is the first study that describes the specific molecular pathways that iPSCs and cancer cells share from a direct comparison" said Paul Knoepfler, associate professor of cell biology and human anatomy, and principal investigator of the study. "It means that much more study is required before iPSCs can be used clinically. However, our study adds to a growing knowledge base that not only will help make stem cell therapies safer, but also provide us with new understandings about the cancer-causing process and more effective ways to fight the disease."
Since 2007, cell biologists have been able to induce specialized, differentiated cells (such as those obtained from the skin or muscle of a human adult) to become iPSCs. Like embryonic stem cells, iPSCs are a type of stem cell that is able to become any cell type. This "pluripotent" capability means that iPSCs have the potential of being used in treatments for a variety of human diseases, a fundamentally new type of clinical care known as regenerative medicine.
iPSCs are considered particularly important because their production avoids the controversy that surrounds embryonic stem cells. In addition, iPSCs can be taken from a patient's own skin and induced to produce other needed tissues, thereby evading the possibility of immunologic rejection that arises when transplanting cells from a donor to a recipient. In contrast to therapies based on ES cells, iPSCs would eliminate the need for patients to take immunosuppressive drugs.
Earlier research indicated that both ES cells and iPSCs pose some health risks. Increasing evidence suggests that pluripotency may be related to rapid cellular growth, a characteristic of cancer. iPSCs, as well as embryonic stem cells, are well known by scientists to have the propensity to cause teratomas, an unusual type of benign tumor that consists of many different cell types. The new UC Davis study demonstrates for the first time that iPSCs -- as well as ES cells -- share significant similarities to malignant cancer cells.
The investigators compared iPSCs to a form of malignant cancer known as oncogenic foci that are also produced in laboratories; these cell types are used by medical researchers to create models of cancer, particularly sarcoma. Specifically, the scientists contrasted the different cells' transcriptomes, composed of the RNA molecules or "transcripts." Unlike DNA analysis, which reflects a cell's entire genetic code whether or not the genes are active, transcriptomes reflect only the genes that are actively expressed at a given time and therefore provide a picture of actual cellular activity.
From this transcriptome analysis, the investigators found that the iPSCs and malignant sarcoma cancer cells are unexpectedly similar in several respects. Genes that were not expressed in iPSCs were also not expressed in the cancer-generating cells, including many that have properties that guide a cell to normally differentiate in certain directions. Both cell types also exhibited evidence of similar metabolic activities, another indication that they are related cell types.
"We were surprised how similar iPSCS were to cancer-generating cells," said Knoepfler. "Our findings indicate that the search for therapeutic applications of iPSCs must proceed with considerable caution if we are to do our best to promote patient safety."
Knoepfler noted, for example, that future experimental therapies using iPSCs for human transplants would most often not involve implanting iPSCs directly into a patient. Instead, iPSCs would be used to create differentiated cells -- or tissues -- in the laboratory, which could then be transplanted into a patient. This approach avoids implanting the actual undifferentiated iPSCS, and reduces the risk of tumor development as a side effect. However, Knoepfler noted that even trace amounts of residual iPSCs could cause cancer in patients, a possibility supported by his team's latest research.
Excerpt from:
Multiple similarities discovered between cancer cells and induced pluripotent stem cells
Researchers Find Similarities Between Cancer Cells And Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
September 30, 2012
April Flowers for redOrbit.com Your Universe Online
A research team from the University of California, Davis, has found evidence that a promising type of stem cell being considered for a variety of disease therapies is very similar to the type of cells that cause cancer. The cells, known as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) show promise as a source of replacement cells and tissues to treat injuries, diseases and chronic conditions. Although the iPSCs have the potential for such good, scientists have to move cautiously because they could also cause malignant cancer, according to the teams study published online in the journal Stem Cells and Development.
This is the first study that describes the specific molecular pathways that iPSCs and cancer cells share from a direct comparison said Paul Knoepfler, associate professor of cell biology and human anatomy. It means that much more study is required before iPSCs can be used clinically. However, our study adds to a growing knowledge base that not only will help make stem cell therapies safer, but also provide us with new understandings about the cancer-causing process and more effective ways to fight the disease.
Cell biologists have been able to induce specialized, differentiated cells such as those obtained from the skin or muscle of adult humans to become iPSCs since 2007. Like embryonic stem cells, iPSCs are pluripotent, meaning they can become any type of cell and have the potential for being used in treatments for a variety of human diseases. This is a fundamentally new type of clinical care known as regenerative medicine.
The production of iPSCs avoids the controversy that surrounds embryonic stem cells (ES), making them particularly important. They can also be taken from a patients own skin and induced to produce other needed tissues, making the chances of immunologic rejection extremely low, eliminating the need to take immunosuppressive drugs.
Earlier studies indicate that both ES and iPSCs pose some health risks. There is an increasing amount of evidence that suggests pluripotency may be related to rapid cellular growth, which is a characteristic of cancer. Both types of stem cells are well known by scientists to have the propensity to cause teratomas, a benign tumor that consists of many different cell types. This new study from UC Davis demonstrates that iPSCs as well as ES cells share significant similarities to malignant cancer cells.
The research team compares iPSCs to a form of malignant cancer known as oncogenic foci that are also produced in laboratories. These are used by scientists to create models of cancer, particularly sarcoma. The scientists contrasted the different cells transcriptomes, comprised of the RNA molecules or transcripts. Transcriptomes reflect only the genes that are actively expressed at a given time and therefore provide a picture of actual cellular activity, unlike DNA analysis, which reflects a cells entire genetic code whether or not the genes are active.
By analyzing the transcriptomes, the team found that the iPSCs and malignant sarcoma cancer cells are unexpectedly similar. Genes not expressed in iPSCs are also not expressed in the cancer-generating cells, including many that have properties that guide a cell to normally differentiate in certain directions. Both cell types also exhibited similar metabolic activities. This is another indication that they are related cell types.
We were surprised how similar iPSCS were to cancer-generating cells, said Knoepfler. Our findings indicate that the search for therapeutic applications of iPSCs must proceed with considerable caution if we are to do our best to promote patient safety.
See the rest here:
Researchers Find Similarities Between Cancer Cells And Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Making it easier to make stem cells
Public release date: 25-Sep-2012 [ | E-mail | Share ]
Contact: Heather Buschman hbuschman@sanfordburnham.org 858-795-5343 Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute
LA JOLLA, Calif., September 25, 2012 The process researchers use to generate induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)a special type of stem cell that can be made in the lab from any type of adult cellis time consuming and inefficient. To speed things up, researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham) turned to kinase inhibitors. These chemical compounds block the activity of kinases, enzymes responsible for many aspects of cellular communication, survival, and growth. As they outline in a paper published September 25 in Nature Communications, the team found several kinase inhibitors that, when added to starter cells, help generate many more iPSCs than the standard method. This new capability will likely speed up research in many fields, better enabling scientists around the world to study human disease and develop new treatments.
"Generating iPSCs depends on the regulation of communication networks within cells," explained Tariq Rana, Ph.D., program director in Sanford-Burnham's Sanford Children's Health Research Center and senior author of the study. "So, when you start manipulating which genes are turned on or off in cells to create pluripotent stem cells, you are probably activating a large number of kinases. Since many of these active kinases are likely inhibiting the conversion to iPSCs, it made sense to us that adding inhibitors might lower the barrier."
According to Tony Hunter, Ph.D., professor in the Molecular and Cell Biology Laboratory at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies and director of the Salk Institute Cancer Center, "The identification of small molecules that improve the efficiency of generating iPSCs is an important step forward in being able to use these cells therapeutically. Tariq Rana's exciting new work has uncovered a class of protein kinase inhibitors that override the normal barriers to efficient iPSC formation, and these inhibitors should prove useful in generating iPSCs from new sources for experimental and ultimately therapeutic purposes." Hunter, a kinase expert, was not involved in this study.
The promise of iPSCs
At the moment, the only treatment option available to many heart failure patients is a heart transplant. Looking for a better alternative, many researchers are coaxing stem cells into new heart muscle. In Alzheimer's disease, researchers are also interested in stem cells, using them to reproduce a person's own malfunctioning brain cells in a dish, where they can be used to test therapeutic drugs. But where do these stem cells come from? Since the advent of iPSC technology, the answer in many cases is the lab. Like their embryonic cousins, iPSCs can be used to generate just about any cell typeheart, brain, or muscle, to name a fewthat can be used to test new therapies or potentially to replace diseased or damaged tissue.
It sounds simple enough: you start with any type of differentiated cell, such as skin cells, add four molecules that reprogram the cells' genomes, and then try to catch those that successfully revert to unspecialized iPSCs. But the process takes a long time and isn't very efficientyou can start with thousands of skin cells and end up with just a few iPSCs.
Inhibiting kinases to make more iPSCs
Zhonghan Li, a graduate student in Rana's laboratory, took on the task of finding kinase inhibitors that might speed up the iPSC-generating process. Scientists in the Conrad Prebys Center for Chemical Genomics, Sanford-Burnham's drug discovery facility, provided Li with a collection of more than 240 chemical compounds that inhibit kinases. Li painstakingly added them one-by-one to his cells and waited to see what happened. Several kinase inhibitors produced many more iPSCs than the untreated cellsin some cases too many iPSCs for the tiny dish housing them. The most potent inhibitors targeted three kinases in particular: AurkA, P38, and IP3K.
Read more from the original source:
Making it easier to make stem cells
Making it easier to make stem cells: Kinase inhibitors lower barrier to producing stem cells in lab
ScienceDaily (Sep. 25, 2012) The process researchers use to generate induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) -- a special type of stem cell that can be made in the lab from any type of adult cell -- is time consuming and inefficient. To speed things up, researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham) turned to kinase inhibitors. These chemical compounds block the activity of kinases, enzymes responsible for many aspects of cellular communication, survival, and growth.
As they outline in a paper published September 25 in Nature Communications, the team found several kinase inhibitors that, when added to starter cells, help generate many more iPSCs than the standard method. This new capability will likely speed up research in many fields, better enabling scientists around the world to study human disease and develop new treatments.
"Generating iPSCs depends on the regulation of communication networks within cells," explained Tariq Rana, Ph.D., program director in Sanford-Burnham's Sanford Children's Health Research Center and senior author of the study. "So, when you start manipulating which genes are turned on or off in cells to create pluripotent stem cells, you are probably activating a large number of kinases. Since many of these active kinases are likely inhibiting the conversion to iPSCs, it made sense to us that adding inhibitors might lower the barrier."
According to Tony Hunter, Ph.D., professor in the Molecular and Cell Biology Laboratory at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies and director of the Salk Institute Cancer Center, "The identification of small molecules that improve the efficiency of generating iPSCs is an important step forward in being able to use these cells therapeutically. Tariq Rana's exciting new work has uncovered a class of protein kinase inhibitors that override the normal barriers to efficient iPSC formation, and these inhibitors should prove useful in generating iPSCs from new sources for experimental and ultimately therapeutic purposes." Hunter, a kinase expert, was not involved in this study.
The promise of iPSCs
At the moment, the only treatment option available to many heart failure patients is a heart transplant. Looking for a better alternative, many researchers are coaxing stem cells into new heart muscle. In Alzheimer's disease, researchers are also interested in stem cells, using them to reproduce a person's own malfunctioning brain cells in a dish, where they can be used to test therapeutic drugs. But where do these stem cells come from? Since the advent of iPSC technology, the answer in many cases is the lab. Like their embryonic cousins, iPSCs can be used to generate just about any cell type -- heart, brain, or muscle, to name a few -- that can be used to test new therapies or potentially to replace diseased or damaged tissue.
It sounds simple enough: you start with any type of differentiated cell, such as skin cells, add four molecules that reprogram the cells' genomes, and then try to catch those that successfully revert to unspecialized iPSCs. But the process takes a long time and isn't very efficient -- you can start with thousands of skin cells and end up with just a few iPSCs.
Inhibiting kinases to make more iPSCs
Zhonghan Li, a graduate student in Rana's laboratory, took on the task of finding kinase inhibitors that might speed up the iPSC-generating process. Scientists in the Conrad Prebys Center for Chemical Genomics, Sanford-Burnham's drug discovery facility, provided Li with a collection of more than 240 chemical compounds that inhibit kinases. Li painstakingly added them one-by-one to his cells and waited to see what happened. Several kinase inhibitors produced many more iPSCs than the untreated cells -- in some cases too many iPSCs for the tiny dish housing them. The most potent inhibitors targeted three kinases in particular: AurkA, P38, and IP3K.
Working with the staff in Sanford-Burnham's genomics, bioinformatics, animal modeling, and histology core facilities -- valuable resources and expertise available to all Sanford-Burnham scientists and the scientific community at large -- Rana and Li further confirmed the specificity of their findings and even nailed down the mechanism behind one inhibitor's beneficial actions.
More:
Making it easier to make stem cells: Kinase inhibitors lower barrier to producing stem cells in lab
Eastday-Shanghai doctors reveal face-change leap
SHANGHAI doctors announced the success of a novel technology that uses people's own skin via stem cells to grow a new face for seriously disfigured patients.
It's an alternative to the surgery used in the West in which doctors transplant the face from a dead body to a patient.
Facial tissue developed with the new technology is more readily accepted physically and psychologically by patients and has no ethical issues, doctors from Shanghai No. 9 People's Hospital said yesterday.
Since adopting the new technology, doctors have used it on more than 60 patients, including seven who needed their whole face replaced or major facial changes.
Of the seven, six were a success, while one case failed as skin on part of the face died, doctors said.
Patients include women disfigured by having sulfuric acid splashed in their faces, people who lost their nose during a fight and a person whose face was seriously burned in a fire.
Under the technology, doctors remove certain blood vessels from the patient's leg to build a small vessel net and transplant it into a place on the body to grow the new face, usually on the a patient's upper chest.
Then doctors use a skin dilator to expand the skin like a bulging ball. Later they inject the patient's own stem cells to help the skin grow stronger and stimulate the growth of blood vessels.
Soft bones which are shaped into facial features like a nose and upper jaw bone in line with the patient's own facial skeleton are then transplanted under the new facial skin.
Finally, the new face is transplanted onto the disfigured face. The new face, which is thin and comprised of a whole piece of living skin, will join with the facial muscles, thus giving a patient natural facial expressions and function to the greatest extent possible.
Read more here:
Eastday-Shanghai doctors reveal face-change leap
Eastday-Shanghai doctors reveal face-change leap
SHANGHAI doctors announced the success of a novel technology that uses people's own skin via stem cells to grow a new face for seriously disfigured patients.
It's an alternative to the surgery used in the West in which doctors transplant the face from a dead body to a patient.
Facial tissue developed with the new technology is more readily accepted physically and psychologically by patients and has no ethical issues, doctors from Shanghai No. 9 People's Hospital said yesterday.
Since adopting the new technology, doctors have used it on more than 60 patients, including seven who needed their whole face replaced or major facial changes.
Of the seven, six were a success, while one case failed as skin on part of the face died, doctors said.
Patients include women disfigured by having sulfuric acid splashed in their faces, people who lost their nose during a fight and a person whose face was seriously burned in a fire.
Under the technology, doctors remove certain blood vessels from the patient's leg to build a small vessel net and transplant it into a place on the body to grow the new face, usually on the a patient's upper chest.
Then doctors use a skin dilator to expand the skin like a bulging ball. Later they inject the patient's own stem cells to help the skin grow stronger and stimulate the growth of blood vessels.
Soft bones which are shaped into facial features like a nose and upper jaw bone in line with the patient's own facial skeleton are then transplanted under the new facial skin.
Finally, the new face is transplanted onto the disfigured face. The new face, which is thin and comprised of a whole piece of living skin, will join with the facial muscles, thus giving a patient natural facial expressions and function to the greatest extent possible.
Soon a stem cell jabs to end wrinkles
London, Sep 10:
Ladies, you may not have to depend upon painful Botox injections and expensive cosmetic surgery for long to look young.
A British firm is trialling a new natural method which involves injecting the patients own stem cells to restore skins youthful elasticity.
Researchers believe they will spur the growth of new skin cells, called fibroblasts, which make the elastic ingredient collagen which is produced in large quantities when we are young, but declines as we age, the Daily Mail reported.
The company Pharmacells, based in Glasgow, plans to begin clinical trials in 12 months, using stem cells harvested from a blood sample from the patients.
They believe the procedure could be commercially available in just three years, potentially revolutionising the market for anti-ageing treatments.
By using the bodys own cells, it is billed as a more natural approach to reducing the signs of ageing than Botox, a chemical which freezes the facial muscles to smooth wrinkles.
The company has licensed the technology to harvest a new type of stem cell called a blastomere-like stem cell (CORR) which is found circulating in the blood.
Like other types of stem cells, it is unspecialised and can develop into many other types of cell in the human body such as a liver, brain or skin cell.
The advantage of this particular one it is available in very large doses from one blood sample.
Originally posted here:
Soon a stem cell jabs to end wrinkles
Could this stem cell cure for wrinkles end the endless hunt for the perfect skin cream?
British firm is trialling new method by injecting patient's own stem cells to restore skin's youthful elasticity
By Tamara Cohen
PUBLISHED: 10:40 EST, 9 September 2012 | UPDATED: 02:12 EST, 10 September 2012
Scientists will begin clinical trials in 12 months, using stem cells harvested from a blood sample from the patients
Scientists are working on a new weapon in the war against wrinkles.
There are not many things women have not tried in the quest for a youthful complexion from lotions and potions to Botox and cosmetic surgery.
But a British firm is trialling a new method which involves injecting the patients own stem cells to restore skins youthful elasticity.
Researchers believe they will spur the growth of new skin cells, called fibroblasts, which make the elastic ingredient collagen which is produced in large quantities when we are young, but declines as we age.
The company Pharmacells, based in Glasgow, plan to begin clinical trials in 12 months, using stem cells harvested from a blood sample from the patients.
They believe the procedure could be commercially available in just three years, potentially revolutionising the market for anti-ageing treatments.
Read the original post:
Could this stem cell cure for wrinkles end the endless hunt for the perfect skin cream?
Introducing Canadians to a whole new way to treat aging skin: Stemulation
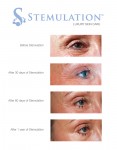
TORONTO, Sept. 10, 2012 /CNW/ - Sigmacon Skin Sciences announced it is the exclusive Canadian distributor of Stemulation, a luxury skin care line that uses the healing power of human stem cells to combat wrinkles and other signs of aging.
Stemulation is based on the science that stem cells can be effectively used for skin rejuvenation, tissue repair and wound healing. A research team of specialists spent two years capturing growth factors from adult human skin cells, which they turned into an active ingredient and the basis for Stemulation products. These growth factors stimulate collagen and the reproduction of new skin cells to reduce wrinkles, eliminate sun spots and smooth scars and fine lines. It truly is a groundbreaking (and technology-backed) new way to achieve younger-looking skin!
The Stemulation line includes a serum, cleanser, exfoliant and face and body creams. The line will be sold through select doctors, estheticians and medical spas.
ABOUT Sigmacon Skin Sciences is the national distributor of a comprehensive set of performance skin care products with dedicated product specialists and trainings all across Canada. Our product lines include professional treatments, sun protection products and results-oriented home care. Sigmacon is also the distributor of advanced medical and aesthetic devices. Visit http://www.skinsciences.ca to learn more.
Image with caption: "The Future of Skin Care: Stemulation Facial Serum and Boost Crme used over 1 year. (CNW Group/Sigmacon Skin Sciences)". Image available at: http://photos.newswire.ca/images/download/20120910_C3135_PHOTO_EN_17420.jpg
Link:
Introducing Canadians to a whole new way to treat aging skin: Stemulation
Scientists Use Skin To Replace Brain Cells Destroyed By Parkinson's [Science]
Parkinson's is a horrible degenerative disorder of the central nervous system which is sadly incurable. But now a team of scientists from Johns Hopkins has been able to grow the brain cells which are usually destroyed by the disease from skin stem cellsand they're confident it will help them develop new treatments.
In fact, their experiments have already been using the lab-grown brain cells to test the effectiveness of drugs currently in development to treat Parkinson's. More exciting, they explain in their report, published in Science Translational Medicine, that the ability to test in the lab should massively speed up the search for new drugs to treat the condition. Ted M. Dawson explains another possibility of the development:
"Our study suggests that some failed drugs should actually work if they were used earlier, and especially if we could diagnose Parkinson's before tremors and other symptoms first appear."
While scientists have in the past been able to halt the disease in mice, none of the compounds used to do so have translated effectively to humans. That suggests that the disease works differently in humans to animals, and makes the new finding all the more useful.
The current thinking is that Parkinson's damages the mitochondria of dopamine neurons in the brain, in effect cutting off their energy supply. The next step for the Johns Hopkins researchers, then, is to investigate how they can slow that damage in the lab-grown cells. [Science Translational Medicine via John Hopkins]
Image by Lasse Kristensen/Shutterstock
Go here to read the rest:
Scientists Use Skin To Replace Brain Cells Destroyed By Parkinson's [Science]
In real time, Yale scientists watch stem cells at work regenerating tissue
Scientists have for the first time watched and manipulated stem cells as they regenerate tissue in an uninjured mammal, Yale researchers report July 1 online in the journal Nature.
Using a sophisticated imaging technique, the researchers also demonstrated that mice lacking a certain type of cell do not regrow hair. The same technique could shed light on how stem cells interact with other cells and trigger repairs in a variety of other organs, including lung and heart tissue.
This tells us a lot about how the tissue regeneration process works, said Valentina Greco, assistant professor of genetics and of dermatology at the Yale Stem Cell Center, researcher for the Yale Cancer Center and senior author of the study.
Greco and her team focused on stem cell behavior in the hair follicle of the mouse. The accessibility of the hair follicle allowed real-time and non-invasive imaging through a technology called 2-photon intravital microscopy.
Using this method, Panteleimon Rompolas, a post-doctoral fellow in Grecos lab and lead author of this paper, was able to study the interaction between stem cells and their progeny, which produce all the different types of cells in the tissue. The interaction of these cells with the immediate environment determines how cells divide, where they migrate and which specialized cells they become.
The technology allowed the team to discover that hair growth in mice cannot take place in the absence of connective tissue called mesenchyme, which appears early in embryonic development.
Stem cells not only spur growth of hair in mammals including humans, but also can serve to regenerate many other types of tissues.
Understanding how stem cell behavior is regulated by the microenvironment can advance our use of stem cells for therapeutic purposes and uncover mechanisms that go wrong in cancer and other diseases, Greco said.
The study was funded by an Alexander Brown Coxe postdoctoral fellowship. This work was supported in part by the American Skin Association and the American Cancer Society and the Yale Rheumatologic Disease Research Core Center and the National Institutes of Health.
Other Yale authors include Elizabeth Deschene, Giovanni Zito, David G. Gonzalez, Ichiko Saotome and Ann M. Haberman.
Continued here:
In real time, Yale scientists watch stem cells at work regenerating tissue
Brain Cells Derived From Skin Cells For Huntington's Research
Editor's Choice Main Category: Huntingtons Disease Also Included In: Stem Cell Research;Neurology / Neuroscience Article Date: 29 Jun 2012 - 14:00 PDT
Current ratings for: Brain Cells Derived From Skin Cells For Huntington's Research
3 (1 votes)
At present, there is no cure for the disease and no treatments are available. These findings open up the possibility of testing treatments for the deadly disorder in a petri dish.
The study is the work of a Huntington's Disease iPSC Consortium, including researchers from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles and the University of California, Irvine, and six other groups.
Huntington's disease is an inherited, deadly neurodegenerative disorder. The onset of HD generally occurs during midlife, although it can also strike in childhood - as in the patient who donated the material for the cells generated in this study. The disease causes jerky, twitch-like movements, lack of muscle control, psychiatric disorders and dementia, and ultimately death.
Christopher A. Ross, M.D., Ph.D., a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, neurology, pharmacology and neuroscience at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and one of the lead researchers of the study, explained:
The team are currently testing small molecules for the ability to block HP iPSC degeneration. According to the researchers, these molecules could potentially be developed into new drugs for Huntington's disease.
Furthermore, the teams ability to create "HD in a dish" may also have implications for similar research in other diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
In the study, the team took a skin biopsy from a 7-year-old patient with very early onset of severe HD. In the laboratory of Hongjun Song, Ph.D., a professor at Johns Hopkins' Institute for Cell Engineering, the skin cells were grown in culture and then created into pluripotent stem cells. In addition, a second cell line was created in the same way in Dr. Ross's lab from an individuals without HD.Simultaneously, other HD and control iPS cell lines were generated as part of the NINDS funded HD iPS cell consortium.
Here is the original post:
Brain Cells Derived From Skin Cells For Huntington's Research
Skin Cells Create Stem Cells In Huntington Disease Study
June 29, 2012
Connie K. Ho for redOrbit.com Your Universe Online
In 1993, the autosomal dominant gene mutation responsible for Huntingtons Disease (HD) was discovered. However, no treatments are known to slow its progression. New research may pave the way to better understanding of the disease. Researchers at Johns Hopkins recently announced that they were able to produce stem cells from skin cells from a person who had severe, early-onset form of HD; the cells were then changed into neurons that degenerated like the cells affected by HD.
The research was recently published in the journal Cell Stem Cell. The investigators worked with an international consortium in creating HD in a dish. The group was made up of scientists from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, the University of California at Irvine, as well as six other groups. The team looked at many other HD cell lines and control cell lines to verify that the results were consistent and reproducible in other labs. The investigators believe that the findings allow them to better understand and eliminate cells in people in with HD. They hope to study the effects of possible drug treatments on cells that would be otherwise found deep in the brain.
Having these cells will allow us to screen for therapeutics in a way we havent been able to before in Huntingtons disease, remarked lead researcher Dr. Christopher A. Ross, a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, neurology, pharmacology and neuroscience at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, in a prepared statement. For the first time, we will be able to study how drugs work on human HD neurons and hopefully take those findings directly to the clinic.
The team of researchers is studying small molecules for the ability to block HD iPSC degeneration to see if they can be developed into new drugs for HD. As well, the ability to produce from stem cells the same neurons found in HD may have effects for similar research in other neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimers and Parkinsons. In the experiment, Ross took a skin biopsy from a patient with very early onset HD. The patient was seven years old at the time, with a severe form of disease and a mutation that caused it. By using cells from a patient who had quickly progressing HD, Ross team were able to mimic HD in a way that could be used by patients who had different forms of HD.
The skin cells were grown in culture and reprogrammed to induce stem cells that were pluripotent. Then, another cell line was created in the same way from someone who didnt have HD. The other HD and control iPS cells were produced as part of the NINDS funded HD iPS cell consortium. Investigators from Johns Hopkins and the other consortium labs changed the cells into typical neurons and then into medium spiny neurons. The process took a total of three months and the scientists found the medium spiny neurons from the HD cells acted how the medium spiny neurons form an HD patient would. The cells demonstrated quick degeneration when cultured in the lab with a basic culture medium that didnt include extensive supporting nutrients. On the other hand, control cell lines didnt demonstrate neuronal degeneration.
These HD cells acted just as we were hoping, says Ross, director of the Baltimore Huntingtons Disease Center. A lot of people said, Youll never be able to get a model in a dish of a human neurodegenerative disease like this. Now, we have them where we can really study and manipulate them, and try to cure them of this horrible disease. The fact that we are able to do this at all still amazes us.
Source: Connie K. Ho for redOrbit.com Your Universe Online
Read the original post:
Skin Cells Create Stem Cells In Huntington Disease Study
Huntington’s Research Tool Developed Using Stem Cells
Main Category: Huntingtons Disease Also Included In: Stem Cell Research Article Date: 28 Jun 2012 - 9:00 PDT
Current ratings for: Huntington's Research Tool Developed Using Stem Cells
Cedars-Sinai scientists have joined with expert colleagues around the globe in using stem cells to develop a laboratory model for Huntington's disease, allowing researchers for the first time to test directly on human cells potential treatments for this fatal, inherited disorder.
As explained in a paper published June 28 on the Cell Stem Cell website and scheduled for print in the journal's Aug. 3 issue, scientists at Cedars-Sinai's Regenerative Medicine Institute and the University of Wisconsin took skin cells from patients with Huntington's disease and reprogrammed them into powerful stem cells; these were then made into the nervous system cells affected by the disease. Seven laboratories around the world collaborated to demonstrate the cells had hallmarks of Huntington's.
"This Huntington's 'disease in a dish' will enable us for the first time to test therapies on human Huntington's disease neurons," said Clive Svendsen, PhD, director of the Cedars-Sinai Regenerative Medicine Institute and a senior author of the study. "In addition to increasing our understanding of this disorder and offering a new pathway to identifying treatments, this study is remarkable because of the extensive interactions between a large group of scientists focused on developing this model. It's a new way of doing trailblazing science."
The Huntington's Disease iPSC Consortium united some of the world's top scientists working on this disease. Cedars-Sinai researchers took skin cells from a several Huntington's patients, including a six-year-old with a severe juvenile form of the disease. They genetically reprogrammed these tissues into induced pluripotent stem cells, which can be made into any type of cell in the body. The cells lines were banked by scientists at Cedars-Sinai and scrutinized by all consortium members for differences that may have led to the disease. These cell lines are now an important resource for Huntington's researchers and have been made available via a National Institutes of Health-funded repository at Coriell Institute for Medical Research in New Jersey.
Huntington's, known to the public, for example, as the cause of folksinger Woody Guthrie's death, typically strikes patients in midlife. It causes jerky, twitching motions, loss of muscle control, psychiatric disorders and dementia; the disease ultimately is fatal. In rare, severe cases, the disorder appears in childhood.
Researchers believe that Huntington's results from a mutation in the huntintin gene, leading to production of an abnormal protein and ultimately cell death in specific areas of the brain that control movement and cognition. There is no cure for Huntington's, nor therapies to slow its progression.
The consortium showed Huntington's cell deficits or how they differ from normal cells, including that they were less likely to survive cultivation in the petri dish. Scientists tried depriving them of a growth factor present around normal cells, or "stressing" them, and found that Huntington's neurons died even faster.
"It was great that these characteristics were seen not only in our laboratory, but by all of the consortium members using different techniques," said Virginia Mattis, a post-doctoral scientist at the Cedars-Sinai Regenerative Medicine Institute and one of the lead authors of the study. "It was very reassuring and significantly strengthens the value of this study."
See the rest here:
Huntington's Research Tool Developed Using Stem Cells
Scientists Correct Huntington’s Mutation in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Newswise Researchers at the Buck Institute have corrected the genetic mutation responsible for Huntingtons Disease (HD) using a human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) that came from a patient suffering from the incurable, inherited neurodegenerative disorder. Scientists took the diseased iPSCs, made the genetic correction, generated neural stem cells and then transplanted the mutation-free cells into a mouse model of HD where they are generating normal neurons in the area of the brain affected by HD. Results of the research are published in the June 28, 2012 online edition of the journal Cell Stem Cell.
iPSCs are reverse-engineered from human cells such as skin, back to a state where they can be coaxed into becoming any type of cell. They can be used to model numerous human diseases and may also serve as sources of transplantable cells that can be used in novel cell therapies. In the latter case, the patient provides a sample of his or her own skin to the laboratory. We believe the ability to make patient-specific, genetically corrected iPSCs from HD patients is a critical step for the eventual use of these cells in cell replacement therapy, said Buck faculty Lisa Ellerby, PhD, lead author of the study. The genetic correction reversed the signs of disease in these cells the neural stem cells were no longer susceptible to cell death and the function of their mitochondria was normal. Ellerby said the corrected cells could populate the area of the mouse brain affected in HD, therefore, the next stage of research involves transplantation of corrected cells to see if the HD-afflicted mice show improved function. Ellerby said these studies are important as now we can deliver patient-specific cells for cell therapy, that no longer have the disease causing mutation.
Huntington's disease (HD) is a devastating, neurodegenerative genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and psychiatric problems. It typically becomes noticeable in mid-adult life, with symptoms beginning between 35 and 44 years of age. Life expectancy following onset of visual symptoms is about 20 years. The worldwide prevalence of HD is 5-10 cases per 100,000 persons. More than a quarter of a million Americans have HD or are "at risk" of inheriting the disease from an affected parent. Key to the disease process is the formation of specific protein aggregates (essentially abnormal clumps) inside some neurons.
All humans have two copies of the Huntingtin gene (HTT), which codes for the protein Huntingtin (Htt). Part of this gene is a repeated section called a trinucleotide repeat, which varies in length between individuals and may change between generations. When the length of this repeated section reaches a certain threshold, it produces an altered form of the protein, called mutant Huntingtin protein (mHtt). Scientists in the Ellerby lab corrected the mutation by replacing the expanded trinucleotide repeat with a normal repeat using homologous recombination. Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination where two molecules of DNA are exchanged. In this case the diseased DNA sequence is exchanged for the normal DNA sequence.
Contributors to the work: Mahru An and Ningzhe Zhang are shared first authors of this study. Other Buck Institute researchers involved in the study include Gary Scott, Daniel Montoro, Tobias Wittkop, and faculty members Sean Mooney and Simon Melov. The work was funded by the Buck Institute and the National Institutes of Health.
About the Buck Institute for Research on Aging The Buck Institute is the U.S.s first and foremost independent research organization devoted to Geroscience focused on the connection between normal aging and chronic disease. Based in Novato, CA, The Buck is dedicated to extending Healthspan, the healthy years of human life and does so utilizing a unique interdisciplinary approach involving laboratories studying the mechanisms of aging and those focused on specific diseases. Buck scientists strive to discover new ways of detecting, preventing and treating age-related diseases such as Alzheimers and Parkinsons, cancer, cardiovascular disease, macular degeneration, diabetes and stroke. In their collaborative research, they are supported by the most recent developments in genomics, proteomics and bioinformatics. For more information: http://www.thebuck.org.
Read more:
Scientists Correct Huntington's Mutation in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells